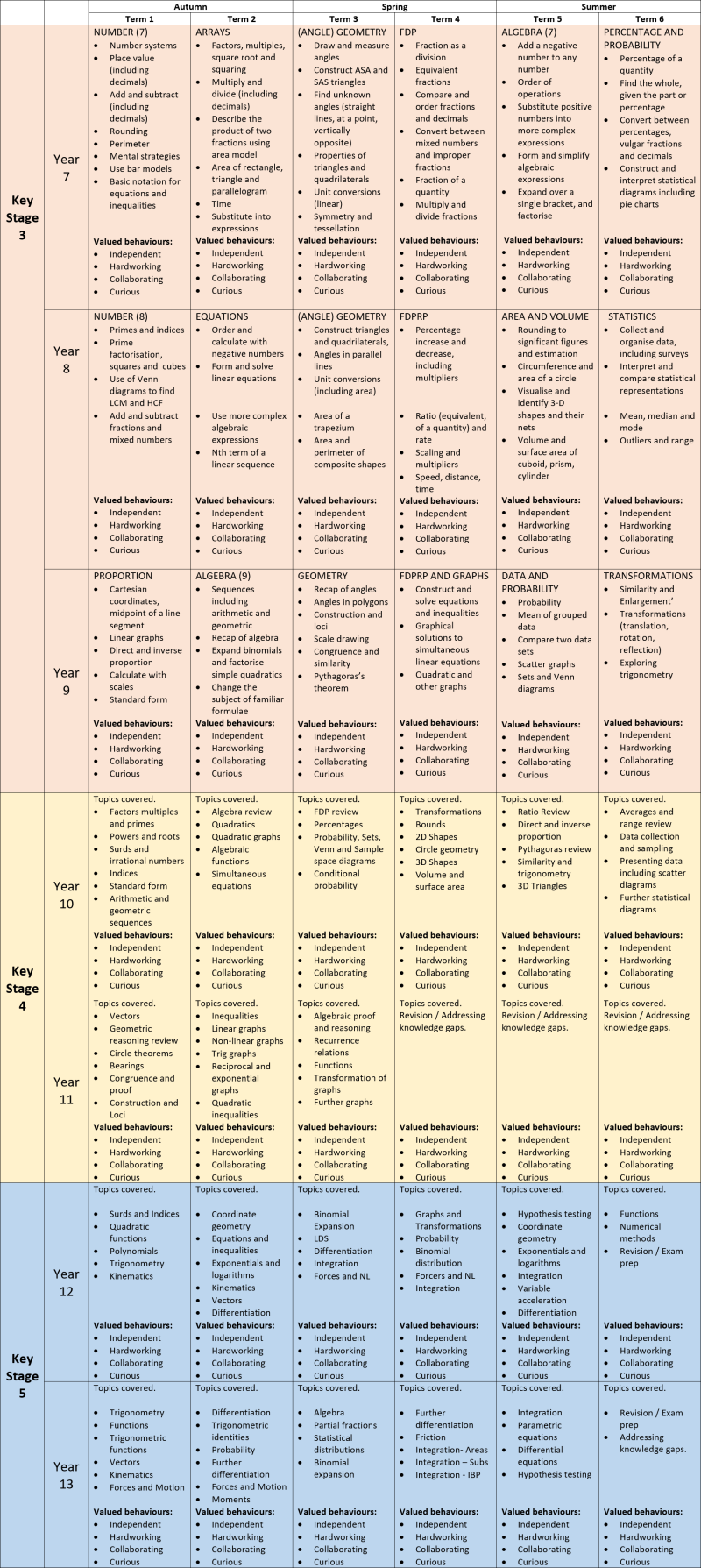
Years 7 to 11 follow the mathematics mastery curriculum. An overview of when we teach which topic can be found under “Curriculum Map”. For further information please contact Mr M. Arhin (marhin@stpetershuntingdon.org)
All KS3 and 4 students sit a test on a half termly basis. The test allows us to diagnose understanding and monitor progress made. You will find feedback for the tests on MyChildatSchool. If you have any queries about the progress of your child please refer to the Contact Us page for email addresses of all teachers in the department.
For the GCSE exam we use the AQA exam board. Students have to sit three papers – each of them 90 minutes long. Paper 1 is a non-calculator paper, in paper 2 and paper 3 the use of a calculator is allowed.
AS Mathematicians follow the AQA AS Mathematics syllabus, studying Pure Maths, Mechanics and Statistics. There are generally no exams at the end of y12 unless it seems necessary. Please refer to the AS and A level support page for recommended support materials.
A Level Mathematicians follow the AQA A2 Mathematics syllabus. The sitting of the AS exam instead of the A2 exam at the end of y12 is at the department’s discretion. The A2 exams are taken in May / June. Please refer to the AS and A level support page for recommended support materials.